Mobilidata Interchange
Introduction
Following the C-Roads architecture, the concept of an interchange is implemented in the Mobilidata environment. The interchange is primarily meant as a low-latency publish-subscribe service to exchange messages with the peripheral functionality. The message-based system is built on an AMQP bus structure that can exchange most message types and is particularly useful for the small mobility messages used in the Mobilidata environment (ETSI C-ITS messages). The communication is IP-based.
Mobilidata Basic Interface (BI)
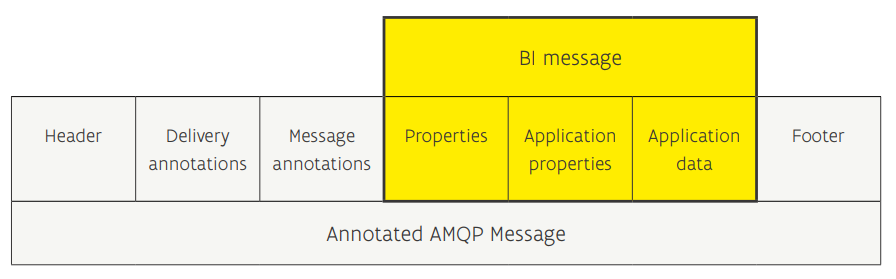
As standard, AMQP uses properties for internal administrative purposes. An application can add specific metadata ( application properties) as well. Within C-Roads, a standard set of metadata is defined (basic interface or BI) that does not take into account road user feedback streams or specific service provider streams. For this reason, a new standard was created: the Mobilidata interface (MI). The MI interface is a superset of the BI interface defined by C-Roads.
Mobilidata Improved Interface (II)
The improved interface is used to detect the remote’s interchange capabilities. No additional features have been defined, which means the Mobilidata II interface is identical to the C-Roads II interface
Access to the AMQP bus is through token-based authorization and whitelisting. A service provider can only read or write in areas for which it has specific rights. In this way, service providers are strictly separated and can only provide the agreed services.